|
Please forgive, when awkward, the English of this page. English is not the author's native language.
Experimental factsWhen light waves are shed onto a photoelectric material, and in specific conditions, a current of electrons is emitted out of the surface of the material.IntroductionThe graphs below represent a photoelectric material, on which light, represented by sinusoidal curves is shed.The characteristics of light are two:
The role of the Wave FrequencyExperimentations show that electrons extraction is exclusively dependent on the wave's frequency of the light hitting the photoelectric material.In short there is a frequency threshold below which no electrons are extracted and frequencies above for which electrons are extracted. It turns out that the violet frequency extracts electrons and red frequency doesn't. Furthermore the higher the frequency of the wave (like ultra-violet), the higher the energy (the speed) of the electrons emitted. 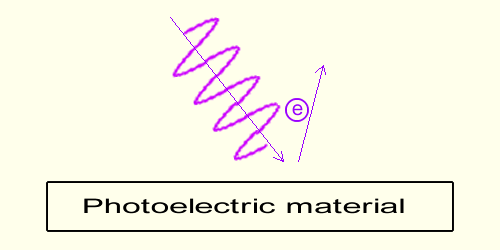 While that speed to frequency dependency is true both in gravimotion and in science physics, beware, the following explanation is not the explanation given in science!
While that speed to frequency dependency is true both in gravimotion and in science physics, beware, the following explanation is not the explanation given in science!The electrons within the material are induced electrically by the wave; any electron encountering the wave gets momentum during the slope increase of the sinusoid in between trough and peak. The time, in which that increase occurs, is obviously dependent on the light frequency. The higher the frequency, the faster the wave's variation, the shorter in a given time the action, the faster the motion induced into the electron. In the end the higher the frequency the higher the energy of the emitted electrons (their speed). WARNING: Even though in science of physics the frequency to speed relationship is the same, the electrons in science are not emitted by way of the variation of the wave; in physics, while light is made of waves as shown here, light is also made of particles-photons (not represented here); and the electrons are knocked-off through brute mechanical collisions, at the image of a billiard ball colliding with another. As already mentioned the frequency of violet light is higher than the frequency of red light. 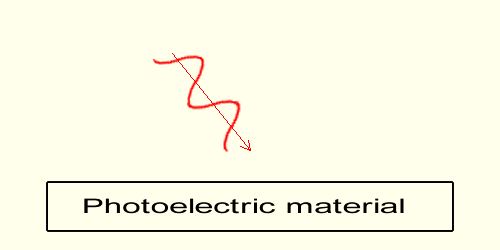 The lower (the redder) the frequency of the wave the flatter the slope of the wave in a given time, the slower the motion induced on the electrons within the material.
The lower (the redder) the frequency of the wave the flatter the slope of the wave in a given time, the slower the motion induced on the electrons within the material.Below a given threshold, which happens to be between violet and red frequencies, no electrons are emitted. On this graph no electron is emitted. And as a general rule, below a given wave frequency, below the threshold, no electrons are emitted. Note that red light nevertheless carries energy; it simply does not carry enough energy to extract an electron from the photoelectric material. The role of Light Intensity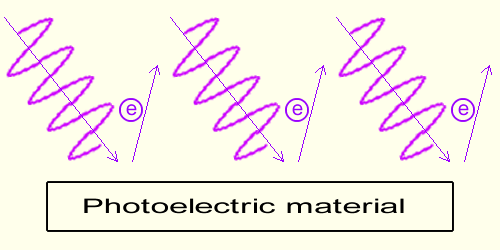 When the wave frequency is above the threshold, (when the frequency permits emission) the higher the intensity of the light wave the higher the number of electrons emitted.
When the wave frequency is above the threshold, (when the frequency permits emission) the higher the intensity of the light wave the higher the number of electrons emitted.Here the graph is made of a light 3 times as bright (3 sinusoids) and 3 electrons are emitted instead of one. Yet all the electrons emitted have the same speed as when only one was emitted. 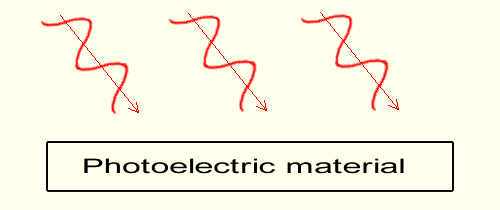
When the wave frequency is below the extraction threshold (red light), electrons are not extracted no matter how high is the intensity of light (fourth graph on right). The red light frequency on this last graph is the same as the one in the second graph above (also red light). Even though the intensity (the light's brightness in the real world) is much higher, the induced speed on the electrons within the material remains the same, too slow for extraction. FOR YOUR INFORMATION in the science of physics the higher intensity is represented, not with a number of waves as done here but with a number of particles photons. In short, the speed of the electrons is always controlled by the frequency, whether electrons are emitted or not. And the number of electrons energized is always controlled by the brightness of light, whether electrons are emitted or not. Einstein's interpretationSince electrons "particles" are dislodged, Einstein declared that the electrons had to be knocked off by "particles"!Einstein theorized that light is made of "particles" that he mathematically defined as packets of energy; and these "light particles" when colliding with electrons provide the later enough speed energy as to overcome the surface barrier of the photoelectric material. Because in "reality", or because the experiments show that the wave's frequency is the cause of emission, Einstein's particle, which has been called the photon since, is "mathematically" made of "frequency". These "frequency" type particles, as any material particle would, allegedly impact mechanically the mass of the electrons and throw the later in motion. Physics' photon acts as if it were made of mass, yet that very photon has no mass in physics! Worse, and most surprisingly, that photon has no electric charge either! And to top it all the photon is dimensionless in science! With no height, no width, and no thickness, having furthermore no mass and being electrically neutral, the questions are: what is the fabric of the photon? Is the photon a real entity? Having no conventional physical characteristic (no dimension, no mass, no electric charge) the photon appears as being a pure mathematical entity. And this mathematical entity, that is this frequency energy is furthermore questionable as it has been created specifically to replace the wave, while not replacing it! The photon is at the origin of the enigmatic concept of light duality. Nevertheless, in physics light waves are still traveling in vacuum and transport their energy, through photons so called particles; particles that are made of nothing, particles that have no mass, no electric charge and that have no physical size! Gravimotion's interpretationYet as shown in the graphs above, there is an extremely simple solution to that light duality and that is unity!You can read much more about it in: |
